
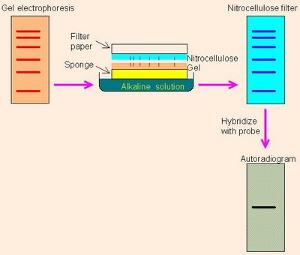
RNA degradation risks because of RNases contamination in work environment.Time consuming (Only one gene can be analyzed at a time).Due to dilution and housekeeping genes control, the results are highly reliable.Detect slightest of gene expression changes due to its sensitivity.Spotted membranes can be stripped of the probes and are reused for hybridization.Relatively simple, cost effective, reduced artifacts.Identify mRNA produced by the transgene to protect recombinants.Detect specific mRNA molecular weights and contents in a sample.Exhibit overexpression of oncogenes and down regulation of tumor suppressor genes in cancerous cells.Diagnosis of several diseases (Crohn’s diseases) including viral infection.Standard for studying and inspecting gene manifestationdesign between tissues, organs, developmental stages, pathogen infection, and over the course of treatment.Northern blotting Applications of Northern Blotting The X-ray film darkens where fragments are corresponding to the radioactive probes.Detection of specific transcript through autoradiography.The membrane is washed in the buffer containing lower concentration of salt to remove excess probes.Hybridization solution should contain 50% formamide to ensure hybridization at lower temperature and minimize RNA degradation.Pre-hybridization blocks single stranded probe from binding on non-specific sites on the membrane.Hybridization is performed using radio or fluorescently labelled probe to identify specific RNA immobilization.Transferred RNA are then immobilized to membrane by baking at 80 ☌ or through UV crosslinking in case of nylon membrane.Electrophoretic transfer method is available only for nylon membrane due to low concentration of salts required to bind the RNA.Vacuum transfer are more efficient but require special transfer apparatus. RNA are transferred via capillary or vacuum transfer.Nitrocellulose and nylons are commonly used membranes.Gels are stained with ethidium bromide after electrophoresis to detect molecular markers and rRNAs.Size of RNA fragments are compared by migration distance with those of molecular weight markers.Separation of RNA is better in glyoxal/DMSO system as sharper band for specific RNA is detected by hybridization.Denaturing agent (formaldehyde or glyoxal/DMSO) disrupts the secondary structure.RNA have secondary structure formed by intramolecular base pairing that prevents RNA from separation according to their size.Separation of RNA using gel Electrophoresis Assessment of quantity and quality of RNA through spectrophotometry.Ģ.RNA isolation by column based technology. Some of the common methods of RNA extraction are:.Multiple ways of isolating RNA but all have some common attributes such as cellular lysis and membrane disruption, inhibiting of ribonuclease activity, deprotenization and recovery of intact RNA.The signals are then detected and visualized using x-films and other methods.A post hybridization wash is required so that the probe is bounded to target mRNA or not is ensured.Finally, hybridization probe is made ready and the probe is hybridized with the membrane.The RNA on the membrane must be immobilized after blotting through baking or exposure under UV light avoiding nucleic acid to wash away later.The derived RNA then undergoes agarose-gel electrophoresis where it gets separated which is then proceeded by blotting onto a nylon membrane.Some cases require the isolation of mRNA from total RNA using a poly-A+ selection procedure. Initially, we extract RNA from a tissue through chaotropic agents such as guanidinium isothiocynate to cause disrupting in cells and denaturing the proteins as well as dissolving the RNA.The fundamental principle of northern blotting is to separate RNA based on their size using gel electrophoresis and identified on a cellular membrane by means of hybridization probe with a base sequence corresponding to all or a part of the chain of the target RNA.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
